Windows Active Directory Interview Questions
>What is Active Directory ?
Active Directory is a Meta Data. Active Directory is a data base which store a data base like your user information, computer information and also other network object info. It has capabilities to manage and administor the complite Network which connect with AD.
>What is domain ?
Windows NT and Windows 2000, a domain is a set of network resources (applications, printers, and so forth) for a group of users. The user need only to log in to the domain to gain access to the resources, which may be located on a number of different servers in the network. The 'domain' is simply your computer address not to confused with an URL. A domain address might look something like 211.170.469.
>What is domain controller ?
A Domain controller (DC) is a server that responds to security authentication requests (logging in, checking permissions, etc.) within the Windows Server domain. A domain is a concept introduced in Windows NT whereby a user may be granted access to a number of computer resources with the use of a single username and password combination.
>What is LDAP ?
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol LDAP is the industry standard directory access protocol, making Active Directory widely accessible to management and query applications. Active Directory supports LDAPv3 and LDAPv2.
>What is KCC ?
KCC ( knowledge consistency checker ) is used to generate replication topology for inter site replication and for intrasite replication.with in a site replication traffic is done via remote procedure calls over ip, while between site it is done through either RPC or SMTP.
>Where is the AD database held? What other folders are related to AD?
The AD data base is store in c:\windows\ntds\NTDS.DIT.
>What is the SYSVOL folder?
The sysVOL folder stores the server's copy of the domain's public files. The contents such as group policy, users etc of the sysvol folder are replicated to all domain controllers in the domain.
>What are the Windows Server 2003 keyboard shortcuts ?
Winkey opens or closes the Start menu. Winkey + BREAK displays the System Properties dialog box. Winkey + TAB moves the focus to the next application in the taskbar. Winkey + SHIFT + TAB moves the focus to the previous application in the taskbar. Winkey + B moves the focus to the notification area. Winkey + D shows the desktop. Winkey + E opens Windows Explorer showing My Computer. Winkey + F opens the Search panel. Winkey + CTRL + F opens the Search panel with Search for Computers module selected. Winkey + F1 opens Help. Winkey + M minimizes all. Winkey + SHIFT+ M undoes minimization. Winkey + R opens Run dialog. Winkey + U opens the Utility Manager. Winkey + L locks the computer.
>Where are the Windows NT Primary Domain Controller (PDC) and its Backup Domain Controller (BDC) in Server 2003 ?
The Active Directory replaces them. Now all domain controllers share a multimaster peer-to-peer read and write relationship that hosts copies of the Active Directory.
>I am trying to create a new universal user group. Why can’t I ?
Universal groups are allowed only in native-mode Windows Server 2003 environments. Native mode requires that all domain controllers be promoted to Windows Server 2003 Active Directory.
>What is LSDOU ? It’s group policy inheritance model, where the policies are applied toLocal machines, Sites, Domains and Organizational Units.
>Why doesn’t LSDOU work under Windows NT ?
If the NTConfig.pol file exist, it has the highest priority among the numerous policies.
>What’s the number of permitted unsuccessful logons on Administrator account? Unlimited. Remember, though, that it’s the Administrator account, not any account that’s part of the Administrators group.
> What’s the difference between guest accounts in Server 2003 and other editions?
More restrictive in Windows Server 2003.
> How many passwords by default are remembered when you check "Enforce Password History Remembered"?
User’s last 6 passwords.
> Can GC Server and Infrastructure place in single server If not explain why ?
No, As Infrastructure master does the same job as the GC. It does not work together.
> Which is service in your windows is responsible for replication of Domain controller to another domain controller.
KCC generates the replication topology.
Use SMTP / RPC to replicate changes.
> What Intrasite and Intersite Replication ?
Intrasite is the replication with in the same site & intersite the replication between sites.
> What is lost & found folder in ADS ?
It’s the folder where you can find the objects missed due to conflict.
Ex: you created a user in OU which is deleted in other DC & when replication happed ADS didn’t find the OU then it will put that in Lost & Found Folder.
> What is Garbage collection ?
Garbage collection is the process of the online defragmentation of active directory. It happens every 12 Hours.
> What System State data contains ?
Contains Startup files,
Registry
Com + Registration Database
Memory Page file
System files
AD information
Cluster Service information
SYSVOL Folder
>What is the difference between Windows 2000 Active Directory and Windows 2003 Active Directory? Is there any difference in 2000 Group Polices and 2003 Group Polices? What is meant by ADS and ADS services in Windows 2003?Windows 2003 Active Directory introduced a number of new security features, as well as convenience features such as the ability to rename a domain controller and even an entire domain
Windows Server 2003 also introduced numerous changes to the default settings that can be affected by Group Policy - you can see a detailed list of each available setting and which OS is required to support it by downloading the Group Policy Settings Reference.
ADS stands for Automated Deployment Services, and is used to quickly roll out identically-configured servers in large-scale enterprise environments. You can get more information from the ADS homepage.
>I want to setup a DNS server and Active Directory domain. What do I do first? If I install the DNS service first and name the zone 'name.org' can I name the AD domain 'name.org' too?
Not only can you have a DNS zone and an Active Directory domain with the same name, it's actually the preferred way to go if at all possible. You can install and configure DNS before installing Active Directory, or you can allow the Active Directory Installation Wizard (dcpromo) itself install DNS on your server in the background.
>How do I determine if user accounts have local administrative access?
You can use the net localgroup administrators command on each workstation (probably in a login script so that it records its information to a central file for later review). This command will enumerate the members of the Administrators group on each machine you run it on. Alternately, you can use the Restricted Groups feature of Group Policy to restrict the membership of Administrators to only those users you want to belong.
>Why am I having trouble printing with XP domain users?
In most cases, the inability to print or access resources in situations like this one will boil down to an issue with name resolution, either DNS or WINS/NetBIOS. Be sure that your Windows XP clients' wireless connections are configured with the correct DNS and WINS name servers, as well as with the appropriate NetBIOS over TCP/IP settings. Compare your wireless settings to your wired LAN settings and look for any discrepancies that may indicate where the functional difference may lie.
>What is the ISTG? Who has that role by default?
Windows 2000 Domain controllers each create Active Directory Replication connection objects representing inbound replication from intra-site replication partners. For inter-site replication, one domain controller per site has the responsibility of evaluating the inter-site replication topology and creating Active Directory Replication Connection objects for appropriate bridgehead servers within its site. The domain controller in each site that owns this role is referred to as the Inter-Site Topology Generator (ISTG).
>What is difference between Server 2003 vs 2008?
1. Virtualization. (Windows Server 2008 introduces Hyper-V (V for Virtualization) but only on 64bit versions. More and more companies are seeing this as a way of reducing hardware costs by running several 'virtual' servers on one physical machine.)
2. Server Core (provides the minimum installation required to carry out a specific server role, such as for a DHCP, DNS or print server)
3. Better security.
4. Role-based installation.
5. Read Only Domain Controllers (RODC).
6. Enhanced terminal services.
7. Network Access Protection - Microsoft's system for ensuring that clients connecting to Server 2008 are patched, running a firewall and in compliance with corporate security policies.
8. PowerShell - Microsoft's command line shell and scripting language has proved popular with some server administrators.
9. IIS 7 .
10. Bitlocker - System drive encryption can be a sensible security measure for servers located in remote branch offices. >br> The main difference between 2003 and 2008 is Virtualization, management. 2008 has more in-build components and updated third party drivers.
11. Windows Aero.
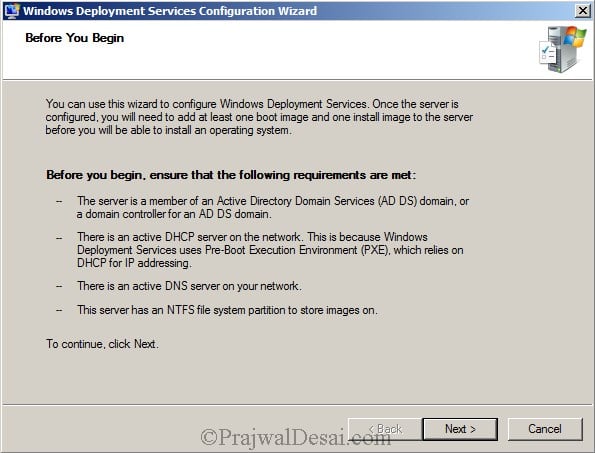
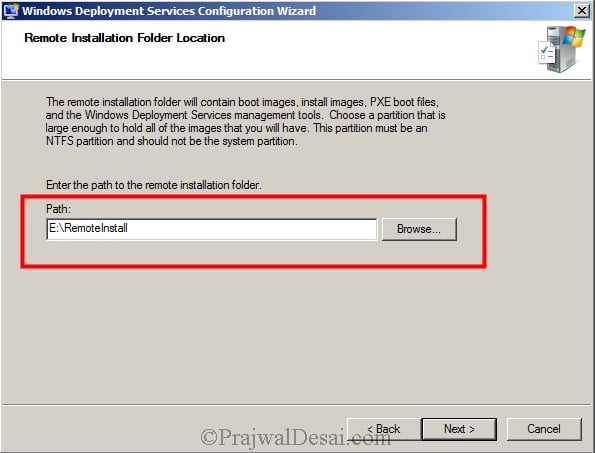
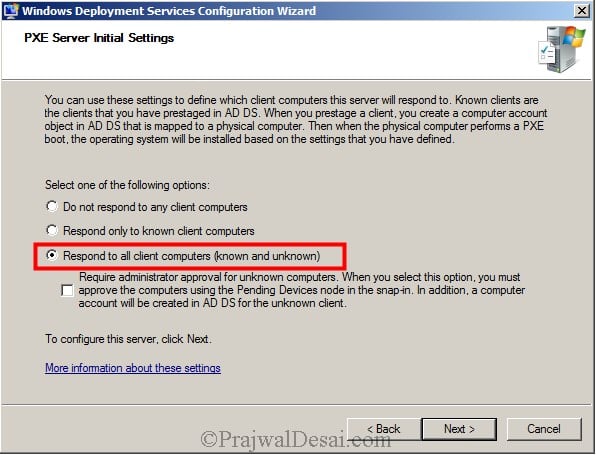
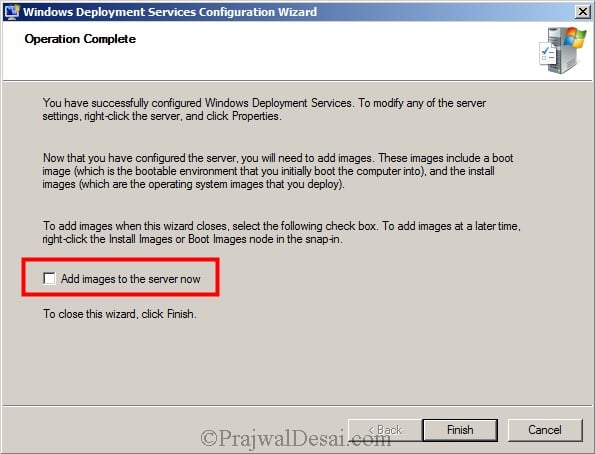
>What are the requirements for installing AD on a new server?
1 The Domain structure.
2 The Domain Name .
3 storage location of the database and log file.
4 Location of the shared system volume folder.
5 DNS config Methode.
6 DNS configuration.
>What is LDP?
LDP : Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) is often used to establish MPLS LSPs when traffic engineering is not required. It establishes LSPs that follow the existing IP routing, and is particularly well suited for establishing a full mesh of LSPs between all of the routers on the network.
>What are the Groups types available in active directory ?
Security groups: Use Security groups for granting permissions to gain access to resources. Sending an e-mail message to a group sends the message to all members of the group. Therefore security groups share the capabilities of distribution groups.
Distribution groups: Distribution groups are used for sending e-main messages to groups of users. You cannot grant permissions to security groups. Even though security groups have all the capabilities of distribution groups, distribution groups still requires, because some applications can only read distribution groups.
>Explain about the groups scope in AD ?
Domain Local Group: Use this scope to grant permissions to domain resources that are located in the same domain in which you created the domain local group. Domain local groups can exist in all mixed, native and interim functional level of domains and forests. Domain local group memberships are not limited as you can add members as user accounts, universal and global groups from any domain. Just to remember, nesting cannot be done in domain local group. A domain local group will not be a member of another Domain Local or any other groups in the same domain.
Global Group: Users with similar function can be grouped under global scope and can be given permission to access a resource (like a printer or shared folder and files) available in local or another domain in same forest. To say in simple words, Global groups can be use to grant permissions to gain access to resourceswhich are located in any domain but in a single forest as their memberships are limited. User accounts and global groups can be added only from the domain in which global group is created. Nesting is possible in Global groups within other groups as you can add a global group into another global group from any domain. Finally to provide permission to domain specific resources (like printers and published folder), they can be members of a Domain Local group. Global groups exist in all mixed, native and interim functional level of domains and forests.
Universal Group Scope: These groups are precisely used for email distribution and can be granted access to resources in all trusted domain as these groups can only be used as a security principal (security group type) in a windows 2000 native or windows server 2003 domain functional level domain. Universal group memberships are not limited like global groups. All domain user accounts and groups can be a member of universal group. Universal groups can be nested under a global or Domain Local group in any domain.
>What is REPLMON ?
The Microsoft definition of the Replmon tool is as follows; This GUI tool enables administrators to view the low-level status of Active Directory replication, force synchronization between domain controllers, view the topology in a graphical format, and monitor the status and performance of domain controller replication.
>What is ADSIEDIT ?
ADSIEDIT :ADSIEdit is a Microsoft Management Console (MMC) snap-in that acts as a low-level editor for Active Directory. It is a Graphical User Interface (GUI) tool. Network administrators can use it for common administrative tasks such as adding, deleting, and moving objects with a directory service. The attributes for each object can be edited or deleted by using this tool. ADSIEdit uses the ADSI application programming interfaces (APIs) to access Active Directory. The following are the required files for using this tool: ADSIEDIT.DLL ADSIEDIT.
>What is NETDOM ?
NETDOM is a command-line tool that allows management of Windows domains and trust relationships. It is used for batch management of trusts, joining computers to domains, verifying trusts, and secure channels.
>What is REPADMIN?
This command-line tool assists administrators in diagnosing replication problems between Windowsdomain controllers.Administrators can use Repadmin to view the replication topology (sometimes referred to as RepsFrom and RepsTo) as seen from the perspective of each domain controller. In addition, Repadmin can be used to manually create the replication topology (although in normal practice this should not be necessary), to force replication events between domain controllers, and to view both the replication metadata and up-to-dateness vectors.
>How to take backup of AD ?
For taking backup of active directory you have to do this : first go START -> PROGRAM ->ACCESORIES -> SYSTEM TOOLS -> BACKUP OR Open run window and ntbackup and take systemstate backup when the backup screen is flash then take the backup of SYSTEM STATE it will take the backup of all the necessary information about the syatem including AD backup , DNS ETC.
>What are the DS* commands ?
The following DS commands: the DS family built in utility .
DSmod - modify Active Directory attributes.
DSrm - to delete Active Directory objects.
DSmove - to relocate objects
DSadd - create new accounts
DSquery - to find objects that match your query attributes.
DSget - list the properties of an object
>What are the requirements for installing AD on a new server?
An NTFS partition with enough free space.
An Administrator's username and password.
The correct operating system version.
A NIC Properly configured TCP/IP (IP address, subnet mask and - optional - default gateway).
A network connection (to a hub or to another computer via a crossover cable) .
An operational DNS server (which can be installed on the DC itself) .
A Domain name that you want to use .
The Windows 2000 or Windows Server 2003 CD media (or at least the i386 folder) .
|